Why ABM?
- Gain the skills to lead transformations in the arts, culture and heritage sectors
- Real-world learning through industry projects to build a stellar portfolio and professional network
- Broad-based curriculum anchored in the creative arts, heritage and event management sectors to give you more career options
- One-year or six-month internship, project work or elective modules – Choose your learning journey in your final year!
About ABM
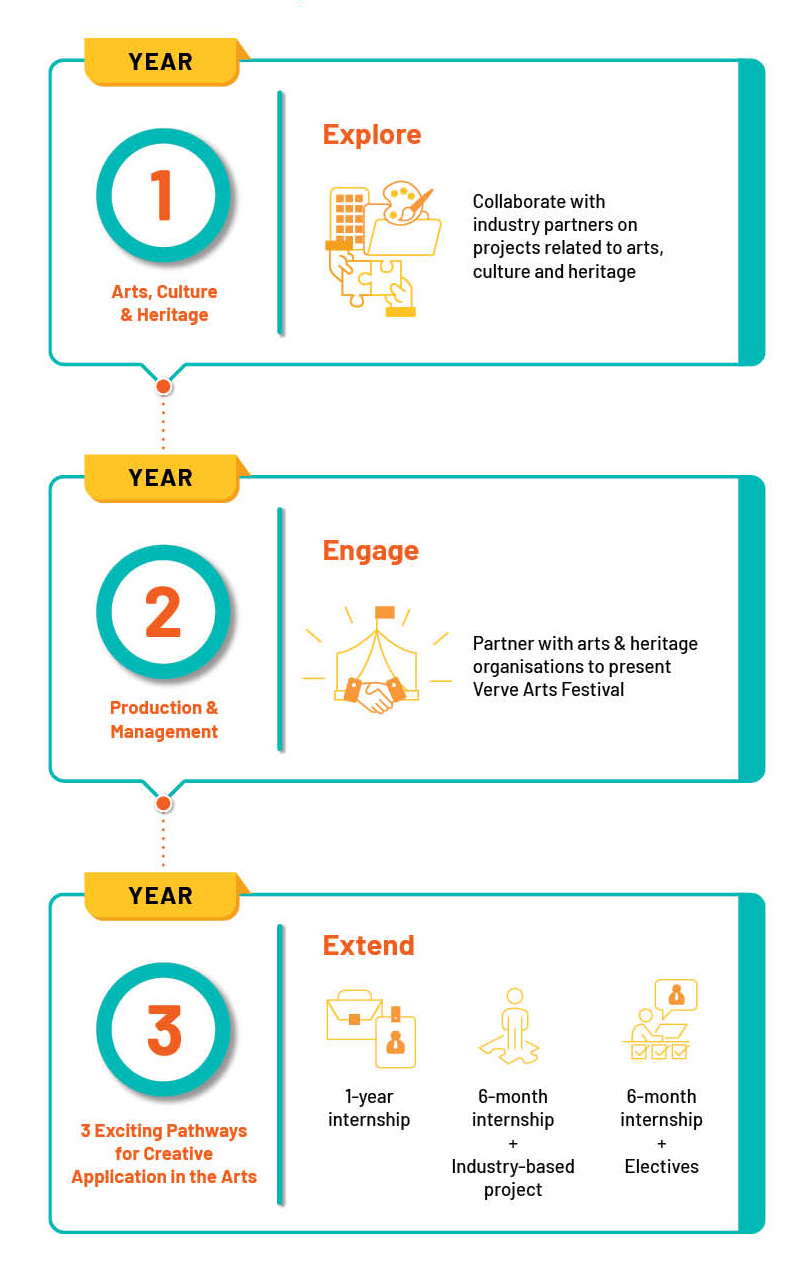
Love the idea of planning arts events or working in galleries, museums, performing arts, or heritage organisations? The Diploma in Arts Business Management (ABM) is what you are looking for! With ABM, you will cultivate an appreciation for various creative art forms – ranging from theatre and music, to dance and visual arts – and gain the business and management skills to thrive in and contribute to the growth of these sectors.
To give you a solid foundation, you will be introduced to business and management skills that will equip you with skills to manage, market and finance arts and heritage organisations. Learn how to conduct research on cultural audiences, use digital media to market your event to different audience segments, develop sponsorship strategies, and organise festivals and events.
In your final year, opt for either a one-year
internship, or a combination of a six-month
internship and project work or elective modules.
Work in the creative industry to conceptualise and
execute business development plans and amass
practical experience that will get you career-ready.
One of the highlights of your ABM journey is the
opportunity to plan and organise Verve, an annual
arts festival. Apply your skills and knowledge to plan
and implement programmes, present arts and cultural
performances, work with artists and volunteers, and
ensure financial sustainability for the event.
Our tie-ups with renowned arts and heritage organisations such as the Singapore Art Museum, Arts House Limited and National Heritage Board will allow you to gain insights into the ins and outs of the local arts and heritage scene. Through industry visits and sponsored projects, prepare to learn from and get inspired by veterans of the arts, culture and heritage fields!


Overview of Your ABM Journey
Further Studies
The broad-based curriculum in ABM offers graduates a wide range of further studies options. Some of the local and overseas universities that our graduates have enrolled in include:
Singapore
- Nanyang Technological University
- National University of Singapore
- Singapore Management University
- Singapore University of Social Sciences
- LASALLE College of the Arts
Australia
- Australian National University
- Monash University
- Queensland University of Technology
- University of New South Wales
- University of Sydney
United Kingdom
- Goldsmiths, University of London
- University of Glasgow
- University of Warwick
Careers
As an ABM graduate, you are professionally trained to manage the creative and heritage industries.
You can look forward to pursuing careers in these job roles:
- Arts Administrator
- Assistant Curator
- Events Executive
- Education and Programmes Executive
- Marketing Executive
- Project Executive
Entry Requirements
AGGREGATE TYPE ELR2B2-B
To be eligible for consideration, candidates must have the following GCE ‘O’ Level examination (or equivalent) results.
| Subject | 'O' Level Grade |
|---|---|
| English Language | 1-6 |
| Additional Mathematics/Mathematics | 1-6 |
| Any one of the 2nd group of Relevant Subjects for the ELR2B2-B Aggregate Type | 1-6 |
Applicants must also fulfil the aggregate computation requirements for the ELR2B2-B Aggregate Type ( English Language, 2 relevant subjects and 2 other best subjects) listed at www.np.edu.sg/docs/ELR2B2.pdf.
For students with other qualifications, please refer to the NP website for the entry requirements and admissions exercise period.
What You Will Learn
Economics (4 Credit Units)
This module provides students with a fundamental understanding of economic principles that shape the creative and cultural industries. It explores the intersection of culture and economics, focusing on how value is created, distributed, and sustained within the creative economy. Students will also learn the impact of cultural activities and develop strategies for cultural management.
Introduction to Heritage, Identity & Community (4 Credit Units) *NEW
This module aims to introduce students to heritage and its intersection with the identity and community. Students will examine how our expressions of heritage are a powerful reflection of both our individual and collective identities. They will also explore methods such as place-making and the creation of heritage experiences to cultivate social bonds and strengthen the community.
Introduction to Visual Arts Management (4 Credit Units) *NEW
This module will aim to provide a foundational understanding of managing the visual arts. Students will examine the various approaches of managing a museum and gallery. Through this, students will study the processes and practices of managing artists, organisations and stakeholders and the artistic work that they present or create.
Academic & Communication Thinking (4 Credit Units)
This module aims to develop students' critical thinking, writing and presentation skills in various academic and professional contexts. Students will also learn how to conduct basic research and accurately cite sources in this module.
Career & Professional Preparation 1 (1 Credit Unit)
This module helps to give students a foundational introduction to their three-year diploma course curriculum and how it prepares them for industry. It will help them to embark on their three-year course with the end in mind, through guided reflection of their personal characteristics and producing an overall game plan for their future education and career goals. The module aims to deepen students’ commitment to the sector that the course prepares them for.
Innovation Made Possible (3 Credit Units)
Underpinned by the Design Thinking framework, Innovation Made Possible aims to build creative confidence in students. The module will sensitize students to the process of user-centric problem solving and allow students to discover and hone their innate ability to think creatively, come up with innovations to tackle problems and explore new ideas for their studies and beyond.
Arts, Heritage & Social Sustainability (4 Credit Units) *RENAMED
This module will explore the impact that the creative sectors can have on society. Topics that will be examined include inclusion, wellness and well-being, and community vitality. Students will develop skills for working with the community to create and conduct programmes that enhance social cohesion and address issues within the community.
Introduction to Performing Arts Management (4 Credit Units) *NEW
This module offers an introductory understanding of the different components of managing the performing arts. The module will study the business side of producing, presenting and promoting performing arts events and activities. These will include an examination of various tasks and roles, such as planning, project management, marketing, and stakeholder management.
Visual Communication (4 Credit Units)
This module offers a foundational understanding of visual literacy and design principles and examines their application in various settings and domains within the creative sector. Students will also explore the ways which visual elements can be used to convey messages effectively, using various online tools and platforms, and in different settings and contexts.
Essential Skills for the Digital Age (4 Credit Units)
This module is designed to help students build critical digital skills needed to succeed in the 21st century. The module covers a range of topics for both the digital workplace and citizenship, including digital communication and collaboration, data investigation and analysis, productivity tools, social media, cybersecurity, responsible use of technology, as well as a roundup of the latest technology trends and future of technology.
Workplace Communication Skills (4 Credit Units)
This module aims to provide students with an understanding of effective communication practices in the workplace. Students will develop the necessary skills to communicate effectively with stakeholders, colleagues, and clients in various communication contexts.
Health & Wellness (1 Credit Unit)
This module aims to help students improve their physical fitness by participating in a physical activity of their choice. This will also give students opportunities to develop confidence, teamwork and leadership.
Exhibition & Experience Development (4 Credit Units) *RENAMED
This module delves into the processes and strategies involved in creating and designing exhibitions and immersive experiences across diverse contexts, including cultural institutions and commercial environments. Students will gain comprehensive knowledge of the various stages of exhibition planning, from initial conceptualization and research to design, production, and final delivery. The module emphasizes innovative approaches to engaging audiences and creating impactful experiences. Students will develop skills in curating content, utilizing cutting-edge technologies, and managing the logistical aspects of exhibition design to design and execute compelling exhibitions and immersive experiences that captivate and educate audiences.
Festival & Event Management (4 Credit Units)
This module aims to develop students’ knowledge and skills in managing arts and entertainment events and festivals. Students will learn how to formulate creative strategies to tackle the complex demands of conceptualising, programming, logistics planning, issues related to policy and regulation, manpower management and risk management. They will also gain insights into the latest management practices in the local as well as the international arts and entertainment and creative sectors.
Marketing & Audience Development (4 Credit Units) * RENAMED
The module examines key marketing concepts and their application to the promotion of artistic products, activities and artists. Students will learn the tools, strategies and approaches to develop audiences and conduct market research. Additionally, they will critically examine the role of social media marketing and acquire skills in using content creation tools to effectively reach audiences.
Partnership Engagement & Volunteer Development (4 Credit Units)
This module provides students with an overview of the fundamentals of stakeholder partnerships, sponsorship and a Volunteer Management Framework in the context of the arts, entertainment, heritage and cultural sectors. Students will gain an understanding of issues related to engaging stakeholders, fund-raising and sponsorship development and the role of the volunteer management framework in managing issues such as volunteers' recruitment, job-match, motivation and recognition.
Career Kickstart (2 Credit Units)
This module is designed to equip students with the skills and knowledge required to successfully navigate the transition from education to the workplace. Topics covered in this module will include job search strategies, resume and cover letter writing, interview skills, professional networking and personal branding.
Artist Management in Arts & Entertainment (4 Credit Units) *NEW
The module examines the crucial role of professional management for various types of artists and entertainers. Focusing on the roles of personal manager, talent
agent, road manager, and company manager, students will learn the art of guiding the professional career of artists, developing contacts within the arts and entertainment sector. They will also navigate issues related to policy and regulation, market
and promote artists for overseas exposure, identify clients and projects for the artists, and negotiate deals.
Arts, Heritage & the Care Economy (4 Credit Units) *NEW
This module explores the intersection of arts, heritage, and the care economy, emphasizing the role of cultural practices in fostering social well-being and community resilience. Students will examine how artistic and heritage activities contribute to
the care economy by enhancing social cohesion, mental health, and community engagement. The module covers key concepts such as cultural heritage management, community arts programmes, and the economic impact of the arts on care services. By the end
of the module, students will be equipped to leverage the arts and heritage sectors to create meaningful social impact and contribute to the care economy.
Creative Entrepreneurship (4 Credit Units)
The module provides students with business fundamentals and skills in the arts and entertainment sector. Students will learn how to start a business, understand different business structures, examine business models, learn about intellectual property
and rights, and create innovative solutions. Students will also learn to combine creative, strategic and entrepreneurial thinking to the development of arts and entertainment enterprises and organisations.
Financial Management (3 Credit Units)
The module introduces the basic concepts of financial management, including accounting, cash management, budgeting, cost behaviour, capital management, in relation to arts organisations. Using case studies, students will learn how to apply financial
accounting principles to the arts industry.
Stage & Venue Management (4 Credit Units) *NEW
This module will equip students with the combined knowledge and skills needed to manage stage productions and venues, focusing on creating business strategies that ensure the viability and sustainability of programs and venues. In stage management, students
will learn key components such as reading a floor plan, floor marking, cueing, and production processes. In venue management, students will treat venues as business entities and will learn critical areas such as front-of-house, back-of-house, ticketing,
venue and business operations, legal aspects, and venue programming.
World Issues: A Singapore Perspective (2 Credit Units)
This module develops a student's ability to think critically on world issues. Students will discuss a wide range of social, political and cultural issues from the Singapore perspective. It also looks at how city-state Singapore defied the odds and
witnessed close to half a century of rapid economic growth, strong political ties and social harmony.
This module provides the opportunity for students to be assigned to industry attachments at reputable organisations. The attachment, which will be for the entire internship semester, will match students’ abilities and interests to relevant organisations.
Project ID aims to prepare you for an increasingly globalized and interconnected world where problems are multi-faceted and require interdisciplinary research and collaboration to solve. Using a project-based learning approach, you will have the opportunity to work in a multi-disciplinary team with students from across the polytechnic to investigate and propose comprehensive recommendations for a pressing real-world problem affecting Singapore. You will be guided to step out of your disciplinary silos and effectively communicate and collaborate with peers from different backgrounds. The module seeks to develop independent learning skills and the ability to synthesize diverse strands of knowledge to solve a complex problem, while impressing on you the importance of being a responsible global citizen.
Description of Elective Modules
Extended Internship (16 Credit Units)
The extended internship allows the student to extend their internship and undergo additional sector relevant on-the-job training in a real-life working environment. In the process, the student will experience working as part of a team and may be exposed to more varied aspects of their chosen area of interest in the sector.
Industry-based Project (16 Credit Units)
For the industry-based project module, students are required to complete a substantial project that is the culmination of their education in the School of Humanities & Interdisciplinary Studies. Students may have the opportunity to work in cross-disciplinary teams to address a real-world problem proposed by a client or proposed by a student in subjects approved by the School.
Social Sustainability (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces students to the social, cultural, and economic dimensions of sustainable development. Students will explore the concepts of sustainability and social responsibility in the context of global and local challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change and the environment. They will learn about the different models of community development, stakeholder engagement, and participatory decision-making that promote social sustainability. The course would also examine the role of businesses and organizations in promoting social sustainability through corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and sustainable business practices. Through case studies, group projects, and interactive discussions, students would develop a critical understanding of social sustainability issues and learn practical skills to address them in their personal and professional lives.
Frameworks for Solutioning (4 Credit Units)
This module will provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the social impact landscape and equip them with practical tools to design and implement effective solutions. The course would introduce students to different frameworks for social impact and to apply these frameworks to social and environmental problems to develop innovative and sustainable solutions that meet the needs of diverse stakeholders. The course would cover topics such as problem definition, research methods, ideation, prototyping, testing, and scaling. Students would also learn about the importance of social impact measurement and evaluation, and how to use data and metrics to assess the effectiveness of their solutions. Through case studies, group projects, and real-world examples, students would develop a deep understanding of the challenges and opportunities of social impact work and acquire the skills and mindset necessary to make a meaningful difference in their communities and beyond.
Understanding Social Challenges (4 Credit Units)
This module provides an interdisciplinary approach to understanding social challenges, such as poverty, inequality and discrimination. Through readings, lectures, discussions, and case studies, students will explore the complex and interrelated causes and consequences of these challenges, as well as potential solutions and interventions.
Understanding Place-Based Challenges (4 Credit Units)
This module provides an interdisciplinary approach to understanding the challenges faced by communities in specific places, such as housing, transportation, safety and land use. Through readings, lectures, discussions, and case studies, students will explore the complex and interrelated causes and consequences of these challenges, as well as potential solutions and interventions.
Communicating to Create Social Change (4 Credit Units)
This module provides an introduction to the art of storytelling and its potential for creating social change. Students will learn how to craft compelling narratives that communicate complex social issues and inspire action. Through readings, lectures, discussions, and hands-on activities, students will explore various forms of storytelling, including visual, written, and oral. The course will also cover topics such as audience analysis, message framing, and impact evaluation.
Digital Strategies for Social Change (4 Credit Units)
This module explores the ways in which technology can be used to advocate for social change. Through readings, lectures, discussions, and hands-on activities, students will learn how to use digital tools and platforms to raise awareness, mobilize support, and influence public policy. The course will cover topics such as social media for outreach, gamification for promoting causes and digital storytelling.









