Why TSE?
- Only diploma of its kind in Singapore taught in Tamil and English
- Attractive Ministry of Education (MOE) Tamil Language Teacher Training Sponsorship (TLTTS) and Early Childhood Development Agency (ECDA) Training Award
- Get certified as a Tamil Mother Tongue Language and English Language preschool educator, with opportunities to be trained at the National Institute of Education to become a Tamil Mother Tongue Language teacher in primary school
About TSE
Are you passionate about making a lasting difference
in children’s lives? Do you have a love for the rich Tamil
language and culture? Make your dream a reality by
taking up the Diploma in Tamil Studies with Early
Education (TSE)!
This one-of-a-kind diploma equips you with the skills
and knowledge to nurture, inspire, educate and care
for the next generation of young minds and share your
passion for the Tamil language and culture with others!
With the importance of Mother Tongue Language in
schools, you will secure good career opportunities as a
Tamil Language preschool educator.
Apply what you have learnt in a six-month internship
at a preschool where you will teach Tamil and English
literacy to young children. The internship also allows
you to develop creative learning activities for children
to improve their literacy and motor skills.
Students enrolled in TSE are eligible for the Tamil Language Teacher Training Sponsorship (TLTTS) and Early Childhood Development Agency (ECDA) Training Award which includes full course fee sponsorship and a monthly allowance of $800!
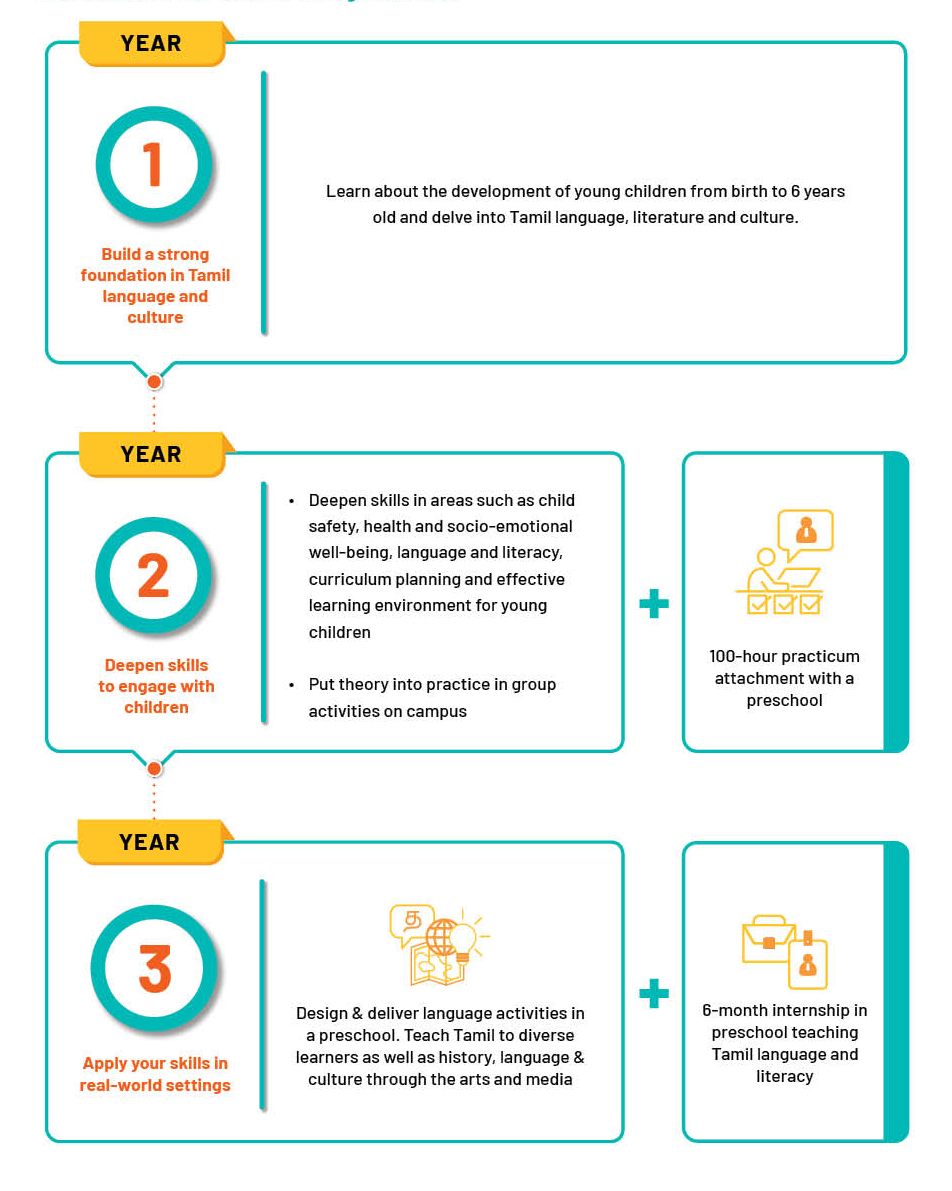
Overview of your TSE Journey
Further Studies
As a TSE graduate, you may apply for further studies in the following universities:
- National Institute of Education / Nanyang Technological University
- Diploma in Education (Tamil Language) (Primary)
- Bachelor of Arts (Academic Discipline & Education) Teaching Scholars Programme
- Bachelor of Arts (Education) – only for candidates selected for MOE Tamil Language Teacher Training Scheme
- National University of Singapore
- Bachelor of Arts in South East Asian Studies (Tamil Studies)
- Singapore University of Social Sciences (SUSS)
- Bachelor of Early Childhood Education with Tamil Language
- Bachelor of Arts in Tamil Language and Literature
Careers
Awarded by NIEC in collaboration with NP, the Diploma in Tamil Studies with Early Education qualifies you as a Level 2 preschool teacher, certified to teach both Tamil and English from Pre-Nursery to K2. You may also apply to MOE to become a primary school Tamil Language teacher if you meet their criteria.
Entry Requirements
AGGREGATE TYPE ELR2B2-A
To be eligible for consideration, candidates must have the following GCE ‘O’ Level examination (or equivalent) results.
| Subject | 'O' Level Grade |
|---|---|
| English Language | 1-6 |
| Higher Tamil or Tamil | 1-4 1-3 |
| Any one of the 1st group of Relevant Subjects for the ELR2B2-A Aggregate Type | 1-6 |
Applicants must also have sat for Additional Mathematics/Mathematics and fulfil the aggregate computation requirements for the ELR2B2-A Aggregate Type ( English Language, 2 relevant subjects and 2 other best subjects) listed at www.np.edu.sg/docs/ELR2B2.pdf.
For students with other qualifications, please refer to the NP website for the entry requirements and admissions exercise period.
Candidates would need to be certified medically fit for study by a certified medical doctor, and to work with children according to ECDA’s medical requirements for preschool teachers.
What You Will Learn
Child Development 1 (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces students to research on brain developments and its implications on children’s growth and learning. Early Years developmental milestones will be discussed with significant emphasis on birth to three years of age. Students will develop an understanding of the philosophy of infant and toddler care and development, and the Early Years Development Framework (EYDF). Theories of child development, with emphasis on Attachment theory, characteristic behaviours, and their implications on play and care-giving practices for families and in the infant care context will be covered. Students will also learn appropriate behaviour guidance and interaction strategies for this age group of children that are guided by observations and documentations.
Communication in Tamil 1 (4 Credit Units)
The module develops the core skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing in Tamil. Students will also learn the technicalities of Tamil language like Tamil word classification and formation of words, grammar, syntax, phonology and semantic, enabling them to be an effective user of the Tamil language.
Introduction to Tamil Culture & Society (3 Credit Units)
This module introduces Tamil heritage and culture, particularly the practices that influences the Tamilians’ way of life in Tamil Nadu, other parts of India and outside of India. Students will also learn about the changes and development of Tamil culture and language over time. Students will be given opportunities to explore ways to promote and preserve Tamil culture and heritage, in the current local context.
Introduction to Tamil Language (3 Credit Units)
This module introduces the development of the Tamil language, setting the foundation for future learning. Students will learn about the origin, history of Tamil language (etymology, Old Tamil, Middle Tamil & Modern Tamil), geographical distribution, spoken and literary variants, writing system, phonology, grammar and vocabulary. They will also learn about the influence Tamil had on other languages.
Motor Skills Development (4 Credit Units)
This module equips students with the knowledge and skills to help young children develop perceptual, fine motor and fundamental movement skills consisting of locomotor, non-locomotor and object control skills in a safe environment. Students will learn to observe, plan, implement and facilitate fun, meaningful and age appropriate indoor and outdoor play activities and fundamental movement experiences using an integrated approach to learning.
This module aims to develop students' critical thinking, writing and presentation skills in various academic and professional contexts. Students will also learn how to conduct basic research and accurately cite sources in this module.
Career & Professional Preparation 1 (1 Credit Unit)
This module gives students a foundational introduction to their three-year diploma course curriculum and how it prepares them for industry. It will help them to embark on their course with the end in mind, through guided reflection of their personal characteristics and producing an overall game plan for their future education and career goals. The module aims to deepen students’ commitment to the sector that the course prepares them for.
Health & Wellness (1 Credit Unit)
This is a Level 1 Core module for all Year 1 students. The module will introduce students to the importance of maintaining both physical and mental health through the knowledge and monitoring of health indicators, and application through appropriate exercises. The aim of the module is to empower students with basic knowledge and skills to be independent and responsible in maintaining overall personal health.
Child Development 2 (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces the major theories in child development and their implications on practices in child-rearing and early care and education. The joint contributions of biology and environment to the various aspects of child development will be explored. Students will deepen their understanding of the holistic development of children through observation, recording and analysis of children’s physical, cognitive, social and emotional growth and development. This understanding will help students link theory to practice and guide the planning of learning experiences and techniques for behaviour guidance. The six learning domains of the Nurturing Early Learners Framework will also be discussed.
Communication in Tamil 2 (4 Credit Units)
The module introduces students to basic translation skills from English to Tamil and vice versa. Students will build on their core skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing in Tamil from the use of technology. These skills will allow students to become effective users of the language in both digital and non-digital platforms.
Principles & Practices in Early Education (4 Credit Units)
This module provides students with an overview of the historical development of early childhood care and education (ECCE), pedagogical principles and contemporary perspectives. Students will also gain an understanding of the different models of practices internationally including the Rights of the Child (UN-CRC) and how they relate to Singapore. ECCE development in the Singapore landscape; policies (of MSF, MOE and ECDA); curriculum frameworks like the Early Years Development Framework and the Nurturing Early Learners: A Curriculum Framework for Kindergartens in Singapore (NEL Framework), as well as SPARK certification that guide provisions of quality care and education and key stage outcomes will also be included. Play that is central to trends and research in ECCE will be explored in the context of how developmentally, culturally and individually appropriate it is as a mode for learning in young children from infancy to the preschool years.
Tamil Literature (3 Credit Units)
The module introduces the Tamil literature from the Sangam period to the Modern era. Students will explore the relationship between Tamil history and its literature. Students will examine the different Tamil epics (e.g. Thirukkural and Aathichudi), local Tamil novels and short stories. Students will be introduced to the elements of Tamil literature, enabling them to reflect and analyze the different literature materials.
Workplace Communication Skills (4 Credit Units)
This
module aims to provide students with an understanding of effective
communication practices in the workplace. Students will develop the
necessary skills to communicate effectively with stakeholders,
colleagues, and clients in various communication contexts.
Essential Skills for the Digital Age (4 Credit Units)
This
introductory module is designed to help students build critical digital
skills needed to succeed in the 21st century. The module covers a range
of topics for both the digital workplace and citizenship, including
digital communication and collaboration, data investigation and
analysis, productivity tools, social media, cybersecurity, responsible
use of technology, as well as a roundup of the latest technology trends
and future of technology.
Aesthetics & Creative Expression (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces students to an array of visual and performing arts. It aims to expose students to the appreciation of the various creative art forms. Students will be introduced to traditional, contemporary and folk art forms like Kolam, Tanjore painting Bharatanatyam, Kuchipudi, Kathakali, Karakattam, Nadaswaram and Mayillatam which are unique to the Tamil and Indian community. In addition, students will be introduced to progressive theories on Arts education to build firm foundations on the key roles the Arts play within early years settings. Theories related to aesthetic and creativity will also be introduced. Students will learn multiple approaches to engage young children in creative-arts expressions in Tamil that are aesthetically rich and imaginative. Through both theory and experiential sessions, students will encounter the Arts first hand and will design Arts experiences that are developmentally appropriate, meaningful and informed by practice.
Child Safety, Health & Socio-emotional Well-Being (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces policies and practices for establishing and maintaining a safe and healthy learning environment for educators and children in early childhood settings as they relate to the socio-emotional well-being of children. Students will understand the importance of nutritional adequacy and balanced meals for children’s optimal growth. They will learn to identify early childhood illnesses and symptoms, engage in hygienic practices, and observe for signs of child abuse and address them professionally. Clinical practice will be included for students to learn how to manage the day-to-day care routines and transitions for children from infancy to the preschool years.
Discovery of the World (4 Credit Units)
This module provides an overview of how young children make sense of the world they live in and how they acquire knowledge and concepts. The scope of Science, environment awareness, technology in everyday life and learning, the Social Sciences, and culture and heritage, will also be covered. Students will learn to use the Constructivist approach to teaching, engage in field exploration and set up discovery corners. Teaching techniques that support enquiry and independent learning in children will be covered. In addition, developmentally and culturally appropriate learning goals and experiences for children from birth to six years of age will be addressed.
Early Numeracy (4 Credit Units)
This module examines the theoretical framework which underpins young children’s learning of mathematics. Students will be introduced to the principles, knowledge and skills required to plan, implement and evaluate learning experiences that lay the foundations for children to become problem solvers and abstract thinkers. Students will learn to choose developmentally appropriate materials and resources, set up a mathematically rich environment, use teaching techniques to nurture children’s mathematical thinking and assess their learning. The use of technology and integration of numeracy in the other learning domains will also be emphasised.
Social Emotional Learning (4 Credit Units)
This module equips students with the theoretical knowledge and pedagogical skills to nurture social-emotional competencies and positive values necessary for character formation in young children. It also addresses the role of teachers in modelling good character traits, in helping children develop self-awareness and self-management skills for their emotional well-being as well as social competence to build strong interpersonal relationships. Students will also take reference from the six learning dispositions (PRAISE) and use children’s picture books to promote positive values, pro-social behaviour, and understanding of self and others; and integrate social emotional learning across the curriculum.
The Professional & Reflective Practitioner (4 Credit Units)
This module explores the various roles of an early childhood educator in working with children, families, other professionals and agencies in the community. A range of professional issues will be examined, including stages of professional development, practitioner competencies, continuing education, advocacy and personal growth plans which are aligned with the current early childhood landscape in Singapore. Students will learn communication and reflective skills and how to manage ethical issues in relation to working with children, colleagues and families taking reference from the Code of Ethics for Early Childhood Professionals by AECES. Students will also be equipped to understand self and reflect on personal preferences and style; develop interpersonal skills and enhance personal effectiveness through self-mentoring.
Curriculum Planning & Implementation (4 Credit Units)
This module provides students with the knowledge and skills for planning, implementing and evaluating developmentally appropriate curriculum in Tamil and English for children from birth to three and from three plus to six years of age. Students will take reference from the Early Years Development Framework, the MOE’s refreshed Kindergarten Curriculum Framework and Nurturing Early Learners: Framework for Mother Tongue Languages to explore the scope and process of integrating learning areas and learning dispositions. Philosophies and beliefs, theoretical underpinnings of how children learn and develop that are fundamental to the meaning of curriculum will be discussed. The supporting environment, the types of learning activities, the role of the educator and different facilitation techniques in Tamil and English will also be thoughtfully considered.
Effective Learning Environment for Young Children (4 Credit Units)
This module equips students with the principles to design conducive learning environments to support play and learning for children from birth to six years of age, noting that the conditions in the environment also affect their behaviour. Students will also learn to set up appropriate learning areas to enhance the physical, cognitive and social and emotional development of children. The selection of print and non-print materials, use of technology and the role of the educator will also be covered.
Language & Literacy (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces students to the theoretical and philosophical underpinnings of language and literacy development from birth to six years of age including trends and issues within a multicultural and multilingual society. Students will learn to design, organise and evaluate a literacy-rich environment that helps facilitate language and literacy development, and identify suitable prints and other media for reading activities to develop in young children an appreciation for a variety of children’s literature. Students will also plan experiences for diverse learners, facilitate learning using appropriate techniques, assess children’s progress and work with families to enhance children’s language and literacy development.
Practicum (2 Credit Units)
Career Kickstart (2 Credit Units)
This module
is designed to equip students with the skills and knowledge required to
successfully navigate the transition from education to the workplace.
Topics covered in this module will include job search strategies, resume
and cover letter writing, interview skills, professional networking and
personal branding.
World Issues: A Singapore Perspective (2 Credit Units)
This module develops a student’s ability to think critically on world issues. Students will discuss a wide range of social, political and cultural issues from the Singapore perspective. It also looks at how city-state Singapore defied the odds and witnessed close to half a century of rapid economic growth, strong political ties and social harmony.
Family & Community Partnership (4 Credit Units)
This module equips students with the knowledge of family structure and dynamics in Singapore and skills for working and communicating with families (focusing in Tamil speaking families), with the understanding of interdependence between schools and families. Various models of family involvement will be explored with a focus on schools working respectfully with diverse family groups and tapping on community resources for the education of young children.
Introduction to Tamil Children’s Literature (3 Credit Units)
The module will be introduced students to the different elements of Tamil literature for children. Students will be given the needed skills and knowledge to appreciate and analyse Tamil children’s literature of different genres such as poems, fairy tales, and fables. Students will explore literature from Tamil Nadu, Singapore and Malaysia. Students will be taught how to design and create suitable literature materials like poem, songs and short stories in Tamil for children.
Tamil History (4 Credit Units)
The module introduced students to Tamil history where students will learn about pre-historic period, Sangam period, Pallava and Pandaya period, Chola period and post-independence period. With this knowledge, students will learn and explore the spread of Tamilians from their original homelands in India during the European, post-colonial and current periods to other regions. Students will learn about the historical, geographical, economic and social factors related to the causes, conditions and outcomes of the migration from India. Through this module, students will gain an understanding of the history of Tamil, allowing them to plan and facilitate suitable learning experience for children enabling them to learn about the history of the Tamil community within and beyond India. It will also equip students with the knowledge and skills to work and communicate with migrant families and children from India.
Tamil Language & Culture through the Arts & Media (3 Credit Units)
This module will provide students with exposure to different arts and media forms such as stage performances, films, podcast and blogs. This will help them develop a deeper understanding of Tamil language and culture in the contemporary society. Themes such as interculturalism, globalisation, and migration will also be introduced to encourage students to critically reflect how they have affected the arts which in turn can be used together with media to promote the learning and acquisition of the Tamil language.
Teaching Tamil to Diverse Learners (3 Credit Units)
The module prepares students for the detailed attention that has to be given to learning the Tamil Language from a young age. It will provide the stepping stone to apply effective instructional methods that are also developmentally appropriate for the teaching of reading, writing and speaking Tamil. Differentiated strategies will be introduced for acquiring vocabulary, comprehension and writing. Students will learn be introduced to types of authentic assessments of and for learning which they can use to collect information to plan and deliver learning experiences creatively based on the language needs of the learners they are working with.
Working with the Exceptional Child (4 Credit Units)
This module introduces students to various exceptional needs in young children including physical, cognitive, behavioural, emotional and sensory characteristics that make them different. Trends and issues in relation to inclusive practices and policies will be covered. Students will learn about their roles in an inclusive learning environment, design of individualised learning plans and communication with families. Students will also explore community resources and professionals that provide support for children with additional needs.
Student Internship Programem (22 Credit Units)
The Internship Programme with professional practitioners acting as mentors enable students to acquire the work experience needed for their chosen areas of interest. The organisations involved are selected for their capacity to allow students to learn different aspects of work in the early childhood industry. The students’ learning outcomes are assessed by their respective internship mentors and NIEC supervisors. Students could also work closely with staff in the early childhood centres on projects that will benefit children, families and the community.
