Why CEP?
- Explore different fields of engineering and discover your interests before deciding on one of our eight diplomas
- Common foundational modules equip you with broad-based fundamental knowledge and skills in engineering
- Unique Induction Programme provides early industry and diploma exposure to help you make an informed course choice
About CEP
If you are keen on engineering but unsure which course
suits you, the Common Engineering Programme (CEP)
may be the perfect fit. Through CEP, you will gain
exposure to different engineering domains, helping you
make a more informed course choice.
In your first semester, you will experience our unique
Induction Programme, which includes learning
journeys, the Diploma Exposure Programme, industry
visits, dialogues, and career advice to help you in
course selection.
You will also build a strong foundation in mechanical,
electronic and electrical engineering, as well as
mathematics and programming. Then, put your new-found knowledge into practice by working on exciting
projects that will boost your portfolio!
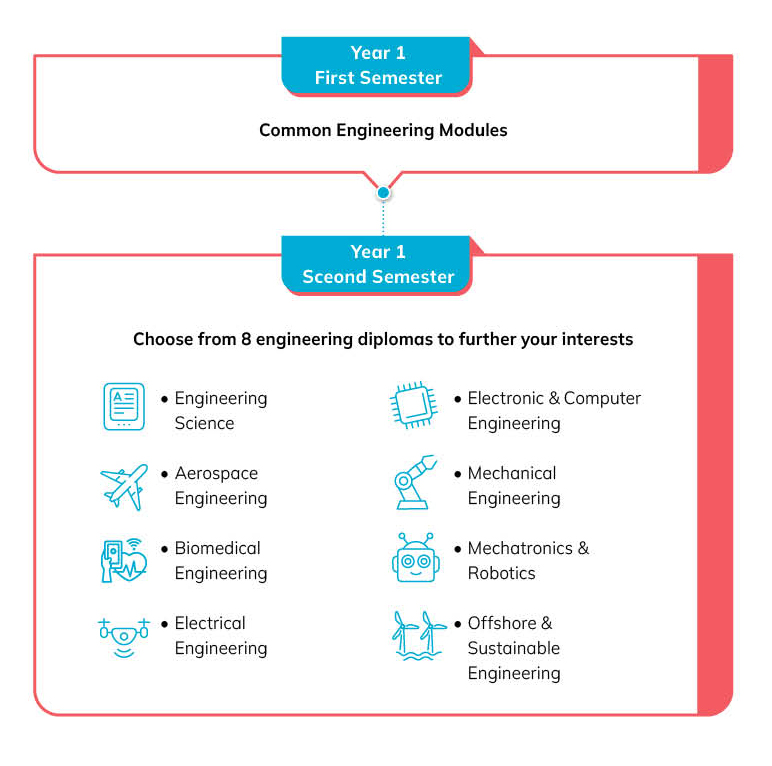
After your first semester, you can choose from one of
our eight engineering diplomas.
Overview of Your CEP Journey
Further Studies
Click here to view the Further Studies options for AEG
Click here to view the Further Studies options for BME
Click here to view the Further Studies options for EE
Click here to view the Further Studies options for ECE
Click here to view the Further Studies options for ES
Click here to view the Further Studies options for ME
Click here to view the Further Studies options for MR
Click here to view the Further Studies options for OSE
Careers
Click here to view the Career options for AEG
Click here to view the Career options for BME
Click here to view the Career options for EE
Click here to view the Career options for ECE
Click here to view the Career options for ES
Click here to view the Career options for ME
Click here to view the Career options for MR
Click here to view the Career options for OSE
Entry Requirements
AGGREGATE TYPE ELR2B2-C
To be eligible for consideration, candidates must have the following GCE ‘O’ Level examination (or equivalent) results.
| Subject | 'O' Level Grade |
|---|---|
| English Language | 1-7 |
| Additional Mathematics/Mathematics | 1-6 |
| Any one of the following subjects: Biology Biotechnology Chemistry Computing/Computer Studies Design & Technology Electronics/Fundamentals of Electronics Physics Science (Chemistry , Biology) Science (Physics, Biology) Science (Physics, Chemistry) | 1-6 |
Applicants must also fulfil the aggregate computation requirements for the ELR2B2-C Aggregate Type ( English Language, 2 relevant subjects and 2 other best subjects) listed at www.np.edu.sg/docs/ELR2B2.pdf .
For students with other qualifications, please refer to the NP website for the entry requirements and admissions exercise period.
Candidates with colour vision deficiency, severe vision deficiency, profound hearing deficiency, uncontrolled epilepsy and/or severe physical impairments may encounter difficulties meeting the course requirements and expectations.
What You Will Learn
Mechanical Engineering Fundamentals
This module introduces students to the study of external forces in two dimensions and their effect on particles and rigid bodies that are at rest and at simple linear motion. Students
learn the knowledge and skills to analyze the forces acting on the bodies by drawing free-body diagrams and applying the conditions of equilibrium. This module also aims to equip students with the skills to analyze problems of rigid bodies in two dimensions
linear motion. Topics include forces and resultants, moments and couples, equilibrium, plane friction, kinematics and kinetics of linear motion.
Electrical Engineering Fundamentals
This module provides a foundation in electricity
covering basic concepts of electrical circuits and the methods used to analyse them. The module emphasises the understanding of the basic electrical circuit laws (Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Voltage and Current Laws) and network theorems, and their
application to electrical network analysis. Topics covered include fundamentals of electricity, network theorems, capacitance, electromagnetic induction and inductance, AC waveform and transformer fundamentals.
Engineering Mathematics 1
This module is designed to provide students with the fundamental skills in mathematics required to solve basic engineering problems. Topics are introduced in an order that is intended to keep abreast of the application requirements in engineering
modules. The emphasis in each topic is on simple applications and problem solving. Topics include algebra, trigonometry, logarithms, plane analytic geometry, matrices and complex numbers. Throughout the module, there is appropriate use of a Computer Algebra
System.
Programming
This practice-oriented module equips students with basic knowledge and skills in computer programming using a suitable high-level language. The main topics include basic computer programming concepts and
fundamental programming constructs such as sequences, selection and repetition.
Career & Engineering Professional Preparation
This module aims to give students a head-start in their professional careers
as they transit into a polytechnic engineering education. The module will equip students with knowledge and skills that can help them chart, navigate and advance in their individual education and career pathways. Students will be guided in adopting a
design thinking approach towards making their education and career plans. They will be exposed to career-centric self-assessment tools and online resources. As part of our efforts to help students benefit from the ubiquity of a professional online presence,
students will also establish their online professional brand by showcasing their marketable knowledge, skills and competencies.
To kickstart our students personal and professional development, the module will also impart various
knowledge and skills, such as, cultural intelligence, financial literacy, digital literacy, industry networking and safety. The topic on safety will be taught according to the Competency Unit “Develop a Risk Management Implementation Plan”
from the Singapore Workforce Skills Qualifications (WSQ) National Competency Standard. To augment this qualification, students will participate in industry engagements and service projects to glean the importance of safety in the engineering profession
and societal context.
Innovation Made Possible^
This module aims to help students discover and hone their innate ability to think creatively and come up with innovations to tackle problems close to their hearts. Underpinned
by the Design Thinking framework, students will be sensitised to the process of user-centric problem solving. They will be introduced to concepts such as empathy, problem-definition, ideation, prototyping and testing through a practical approach featuring
engaging out-of-classroom activities, just-in-time master-classes and a hands-on, “learning by doing” delivery format. Ultimately, the module will help students recognise that innovation is attainable and fun and develop creative confidence
to explore new ideas in their studies and beyond.
^ Critical Core modules account for 13 credit units of the diploma curriculum. They include modules in communication, innovation and world issues, as well as an interdisciplinary project. By bringing students from diverse diplomas together, the interdisciplinary project fosters collaboration to explore and propose solutions for real-world problems. NP aims to develop students to be agile and self-directed learners, ready for the future workplace.
